
BPS has been a trusted supplier of VRLA battery for over 12 years! Some of the things we encounter every day may be new to you. Hereby we have collected some of the frequently asked questions with regards to batteries below. If you have a question beyond what you see below, please contact us by dropping us an email support@bps-battery.com.
11. Can AGM battery be installed in any position?
The AGM and Gel batteries can be mounted on their sides with no problems, but should not be mounted upside down.
12. Why is the charging voltage for "cycle use" higher that the voltage used for "standby use"?
Cycle use is a direct power source. The charging time can not be too long for a user. The higher charging voltage can provide longer maximum charging current during the charging period. (A full charge should be Charging AH / Discharging AH = 110% ~ 120%.)
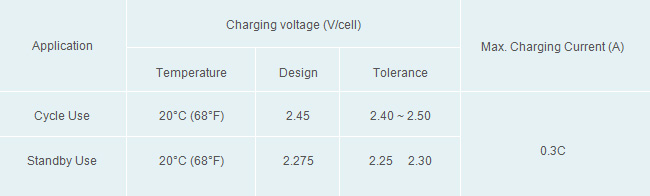
13. What is the effect of different charging currents on batteries?
A higher charging current can shorten charging time. However, a higher charging will cause more heat and gas inside the battery and could result in thermal runaway. The suggested charging current for our battery is no more than 0.3CA.
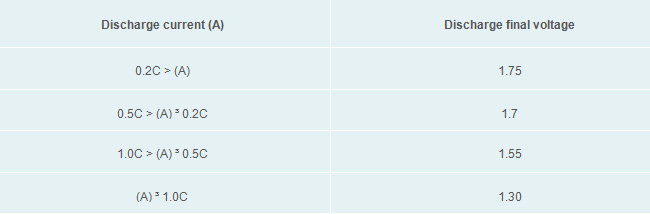
14. What does "100% discharge" and "50% discharge" mean?
To illustrate, use a fixed load to discharge(W or A). If the discharge time is 10 minutes until the voltage comes down to the final voltage then we can say it is 100% discharged. In the same way, if the discharge time is 5 minutes then it is 50% discharged. The table below shows the relationship between "discharge current" and "final voltage."
15. Thermal runaway will happen if a battery is operated under 40-50°C for a long period. How will thermal runaway effect a battery?
As a result of too high a charge voltage, excessive current will flow into the battery, after reaching full charge causing decomposition of water in the electrolyte and premature aging, At high rates of overcharge a battery progressively heat up. As the battery gets hotter it will accept more current heating up even further. This is called thermal runaway and it can destroy a battery in a few hours, battery swelling and result in a dangerous condition. BPS does not recommend to use the batteries for a long time under high temperature environment.
16. How can you check to see if a battery has been fully charged?
Please see the answer to question No.11..
17. What are the concerns when using BPS batteries in a parallel or a serial?
Do not mix brands, models and date codes.
No separate discharge then charging in a serial configuration.
Under parallel usage, pay close attention to the differences in voltage in each circuit.
If the difference in voltage in each circuit is too high, do not charge/discharge as parallel.
The environment of all circuits must be similar.
18. How to check a battery's performance?
Different usage applications will use different methods for evaluating a battery's performance. Using a 20 hour rate or the 10 hour rate, you can use 0.05CA or 0.1CA to discharge the battery until the battery reaches a terminal voltage of 10.25 volts. You can then calculate the amp hours to see if the battery fits the specifications or not. For a 5 minutes rate, such as the 12V5AH, you can use a 21 watts/cell discharge till the terminal voltage reaches a terminal voltage of 9.6 volts and then measure the discharge time to see if it meets the final specifications or not.
19. Why "zero voltage" might happen?
Zero voltage means there is a broken circuit. There could be several reasons for a zero voltage state.
1.There could be a broken electrode column
2.Welding defects of the partition
3.Welding defects of the terminal
20. What is the proper way to test a battery?
Step 1: Disconnect the battery from any power source, this is for your safety. A battery connected to a power source can cause electrical shock or burns.
Step 2: If you’re DC volt meter has a knob setting, set it to a value higher but close to the voltage rating of your battery. For example, if a battery has a voltage rating of 6 volts set it to 10 and if a battery has a voltage rating of 12 volts set it to 20. If you’re DC volt meter does not have setting insure that it can read values higher than the voltage rating of your battery with a range of at least 4 volts above the voltage rating of the battery to be tested.
Step 3: Connect the probes of the DC volt meter to the matching color posts on the battery and note the reading. If the battery is a 12 volt rated battery it should read above 12.5 volts if the battery is good and if the battery is a 6 volt rated battery it should read above 6.5 volts if the battery is good.
Note: The reason it should read higher than its volt rating is due to the batteries construction and shows that it is currently holding a charge. If a battery reads only its volt rating after charging has been attempted, it cannot hold a charge and should be replaced.
 BPS has been a trusted supplier of VRLA battery for over 12 years! Some of the things we encounter every day may be new to you. Hereby we have collected some of the frequently asked questions with regards to batteries below. If you have a question beyond what you see below, please contact us by dropping us an email support@bps-battery.com.
BPS has been a trusted supplier of VRLA battery for over 12 years! Some of the things we encounter every day may be new to you. Hereby we have collected some of the frequently asked questions with regards to batteries below. If you have a question beyond what you see below, please contact us by dropping us an email support@bps-battery.com. 

